Introduction
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Monetary Policy 2025 has introduced key adjustments aimed at strengthening economic stability and fostering growth. The repo rate has been reduced to 6.25%, signaling a strategic move to enhance liquidity and drive consumer demand. Additionally, the Standing Deposit Facility rate is now set at 6%, while GDP growth for 2025 is projected at 6.4%. This comprehensive guide explores the major policy updates, their implications, and what they mean for businesses and consumers alike.
Key Highlights of RBI Monetary Policy 2025
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) met on February 7, 2025, and decided unanimously to adjust the policy framework. Below are the most significant updates:
- Repo rate cut: Reduced by 25 basis points, from 6.5% to 6.25%.
- Standing Deposit Facility rate: Adjusted to 6%.
- Inflation outlook: Expected to gradually align with the 4% target in 2025-26.
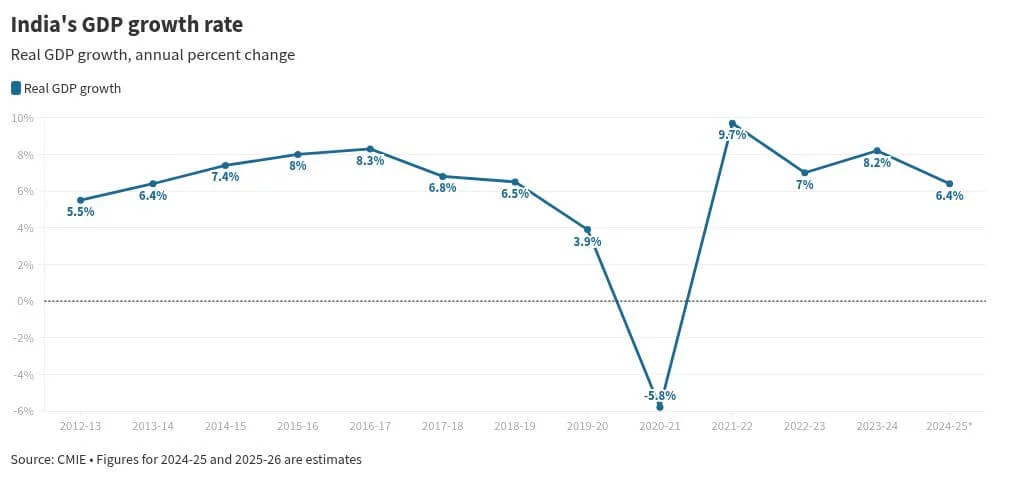
- Real GDP growth forecast: Estimated at 6.4% for the financial year.
- Neutral policy stance: RBI aims to balance inflation control and economic growth.
- Global headwinds: Caution over geopolitical uncertainties, trade tensions, and market volatility.
- Agriculture & manufacturing growth: Positive indicators suggest a recovery in the latter half of the year.
- Urban demand & employment: Expected improvements following tax relief in the Union Budget 2025.
- Food inflation: Likely to stabilize, driven by a favorable Rabi crop outlook.
Impact of the Policy on the Economy
The latest monetary policy decisions will have far-reaching implications across multiple sectors. Below are the anticipated effects:
1. Interest Rates & Borrowing Costs
With a repo rate cut to 6.25%, banks are likely to reduce loan and mortgage interest rates, making credit more accessible for businesses and consumers. This move is expected to boost investments and spending, particularly in sectors such as real estate and automobile manufacturing.
2. Inflation Control Measures
Despite persistent concerns about global uncertainties, inflation levels are expected to moderate. RBI projects a 4.2% inflation rate for 2025-26, assuming normal monsoon conditions and steady commodity prices. A stable inflation outlook fosters consumer confidence and encourages spending.
3. GDP Growth & Industrial Performance
The GDP growth projection of 6.4% aligns with positive industrial trends. Manufacturing and agriculture are set to gain momentum, with early Q3 indicators showing signs of recovery. Additionally, resilient business sentiment suggests that services will remain strong, despite a slight dip in the Services PMI index.
4. Employment & Consumer Spending
With improved economic sentiment, the employment landscape is expected to strengthen. The Union Budget’s tax relief measures, coupled with lower borrowing costs, should boost household consumption, driving demand in retail and e-commerce sectors.
5. Global Economic Challenges & RBI’s Response
Despite domestic optimism, global economic headwinds remain a concern. Uncertainties in international trade policies, financial market fluctuations, and adverse weather patterns could pose risks. However, the RBI’s neutral stance ensures flexibility in policy adjustments, allowing for strategic interventions when needed.
Final Thoughts: What Lies Ahead?
The RBI Monetary Policy 2025 presents a balanced approach, addressing economic growth, inflation control, and financial stability. With a focus on maintaining liquidity while supporting long-term development, the new policy framework sets the stage for a resilient and dynamic economic outlook in the coming year.


